Your gut is a complex and fascinating part of your body, responsible for breaking down the food you eat and absorbing the nutrients your body needs. But did you know that your gut is also home to trillions of bacteria that play a crucial role in your overall health and well-being? From maintaining a healthy weight to regulating your immune system, the health of your gut can have a significant impact on your overall health. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at your digestive system, exploring how it works, what can go wrong, and how you can keep your gut healthy for optimal well-being. Whether you’re dealing with digestive issues or simply looking to improve your overall health, this guide will provide you with everything you need to know about your gut.
Table of Contents
What is Digestive system?
The digestive system is a group of organs responsible for breaking down food into nutrients that can be absorbed by the body. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. The digestive system also includes accessory organs such as the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder, which produce and release digestive enzymes and other substances that aid in digestion.
How does Digestive system Works ?
The digestive system is responsible for breaking down the food we eat into smaller molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body for energy, growth, and repair. The digestive system is made up of several organs and structures, each of which plays a unique role in the process of digestion.
The digestive process begins in the mouth, where food is broken down into smaller pieces by the teeth and mixed with saliva, which contains enzymes that help to break down carbohydrates. From there, the food travels down the esophagus to the stomach, where it is mixed with gastric juices that break down proteins and further break down carbohydrates. The stomach also regulates the release of food into the small intestine, where most of the nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream.
The small intestine is where most of the digestion and absorption takes place. It is lined with tiny finger-like projections called villi, which increase the surface area for absorption. Nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to the liver, where they are further processed and distributed throughout the body.
The remaining undigested food particles move on to the large intestine, where water is absorbed and waste products are eliminated from the body through the rectum and anus.
How to keep digestive system healthy?
To keep the digestive system healthy, it is important to follow a balanced diet, rich in fiber, and to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. Fiber can help to regulate bowel movements and prevent constipation, which can lead to digestive problems. Drinking water helps to keep the digestive tract hydrated and functioning properly.
Regular exercise can also help to keep the digestive system healthy by promoting the movement of food through the digestive tract. In addition, stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help to reduce stress-related digestive issues such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also help to maintain a healthy digestive system. These habits can damage the lining of the digestive tract and increase the risk of digestive diseases such as ulcers and cancer.
Finally, it is important to practice good hygiene habits such as washing your hands regularly to prevent the spread of harmful bacteria that can cause digestive infections.
The Organs of the Digestive System: What They Are and What They Do?
The digestive system is made up of several organs and structures, each of which plays a unique role in the process of digestion. Here is a breakdown of the major organs and structures of the digestive system, and what they do:
- Mouth: The mouth is where digestion begins. The teeth break down food into smaller pieces, and saliva contains enzymes that start to break down carbohydrates.
- Esophagus: The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. It moves food from the mouth to the stomach through a series of muscle contractions known as peristalsis.
- Stomach: The stomach is a muscular sac that mixes food with gastric juices, which contain enzymes and acids that break down proteins and further break down carbohydrates.
- Small intestine: The small intestine is a long, narrow tube that is divided into three sections: the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum. This is where most of the digestion and absorption takes place. The walls of the small intestine are lined with tiny finger-like projections called villi, which increase the surface area for absorption.
- Liver: The liver produces bile, which helps to break down fats in the small intestine.
- Gallbladder: The gallbladder stores and releases bile into the small intestine.
- Pancreas: The pancreas produces enzymes that help to break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
- Large intestine: The large intestine, also known as the colon, absorbs water from waste products and eliminates them from the body through the rectum and anus.
Each of these organs and structures plays a crucial role in the process of digestion. Any disruptions or issues with one of these organs or structures can lead to digestive problems and health issues. It is important to maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle to support optimal digestive health.
The Role of Enzymes in Digestion: Breaking Down Food for Absorption
Enzymes play a crucial role in the process of digestion by breaking down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body. Enzymes are specialized proteins that act as biological catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions in the body.
There are several types of enzymes involved in the digestive process, each with a specific role to play. Here are a few examples:
- Amylase: This enzyme breaks down carbohydrates into simple sugars, such as glucose.
- Protease: This enzyme breaks down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids.
- Lipase: This enzyme breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
Enzymes are produced by various organs in the digestive system, including the salivary glands, stomach, pancreas, and small intestine. Enzyme production is stimulated by the presence of food, and different enzymes are produced depending on the type of food being eaten.
Once food is broken down by enzymes, the resulting smaller molecules can be absorbed by the body and used for energy, growth, and repair. For example, glucose is used as a primary source of energy for the body’s cells, while amino acids are used to build and repair muscles and other tissues.
However, if enzyme production is disrupted or inadequate, digestion can be impaired. This can lead to a range of digestive problems, including bloating, gas, and diarrhea. In some cases, enzyme supplements may be recommended to help support digestion and improve overall digestive health.
Conclusion
Overall, enzymes play a crucial role in the process of digestion by breaking down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body. Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle can help to support optimal enzyme production and digestive health.
The Importance of Fiber in Digestive Health: How Much You Need and Where to Find It
Fiber is an essential nutrient for digestive health, as it plays a crucial role in promoting regularity, preventing constipation, and supporting overall gut health. Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest, meaning it passes through the digestive system relatively intact, providing bulk and promoting bowel movements.
There are two main types of fiber: soluble fiber and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like substance in the digestive tract, which can help to lower cholesterol levels and regulate blood sugar. Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water and adds bulk to the stool, helping to promote regularity and prevent constipation.
So, how much fiber do you need? The recommended daily intake of fiber is around 25-30 grams for adults. However, most people in the Western world consume only half that amount or less. Increasing your fiber intake gradually can help prevent bloating, gas, and other digestive issues that can result from a sudden increase in fiber intake.
Good sources of fiber include:
- Whole grains: Whole wheat, brown rice, quinoa, and oats are all great sources of fiber.
- Fruits and vegetables: Fresh fruits and vegetables are high in fiber, as well as vitamins and minerals. Berries, apples, bananas, broccoli, carrots, and sweet potatoes are all good choices.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and peas are all excellent sources of fiber and protein.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds are all high in fiber.
Conclusion
Adding more fiber-rich foods to your diet can help to support digestive health and prevent a range of digestive issues. However, it’s important to drink plenty of water when increasing your fiber intake, as fiber absorbs water and can lead to dehydration if you don’t drink enough.
Hydration and Digestion: Why Drinking Enough Water Is Key to a Healthy Digestive System
Water is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system, as it plays a crucial role in helping the body to break down food, absorb nutrients, and eliminate waste. When you don’t drink enough water, digestion can be impaired, leading to a range of digestive issues.
Here are some of the ways in which hydration is important for digestive health:
- Digestion: Water is necessary for breaking down food and aiding in the absorption of nutrients. Without enough water, food can move through the digestive tract more slowly, leading to constipation and other digestive issues.
- Bowel movements: Water helps to soften stools and makes them easier to pass, reducing the risk of constipation.
- Nutrient absorption: Water is necessary for the absorption of nutrients from food. When you don’t drink enough water, your body may not be able to absorb nutrients effectively, leading to nutrient deficiencies.
- Waste elimination: Water helps to flush waste products out of the body, reducing the risk of constipation and other digestive issues.
So, how much water should you drink for optimal digestive health? The recommended daily intake of water varies depending on factors such as age, sex, and activity level, but a general guideline is to aim for around 8-10 glasses of water per day.
In addition to drinking water, you can also stay hydrated by eating water-rich foods, such as fruits and vegetables. Examples include watermelon, cucumbers, lettuce, and citrus fruits.
Conclusion
Overall, staying hydrated is key to maintaining a healthy digestive system. Drinking enough water can help to promote regularity, prevent constipation, and support the absorption of nutrients, leading to improved digestive health and overall well-being.
How CBD Salve is Made - A detailed explanation of the process of making CBD salve.
Have you ever wondered how CBD salve is made? In this article, we’ll take a detailed look at the process of making CBD salve, including the extraction of CBD oil, the selection of other ingredients, and the manufacturing process.
- Step 1- Extracting CBD Oil: The first step in making CBD salve is to extract the CBD oil from the hemp plant. There are several methods for extracting CBD oil, but the most common method is CO2 extraction. This involves using supercritical carbon dioxide to extract the CBD oil from the hemp plant, resulting in a pure and potent CBD extract.
- Step 2- Selecting Other Ingredients: Once the CBD oil has been extracted, it’s time to select other ingredients for the CBD salve. These can vary depending on the intended use of the salve, but common ingredients include carrier oils, such as coconut oil or olive oil, and essential oils, such as lavender or peppermint oil. Other ingredients may also be added for specific purposes, such as arnica for pain relief or shea butter for moisturization.
- Step 3- Manufacturing Process:With the CBD oil and other ingredients selected, it’s time to manufacture the CBD salve. The manufacturing process can vary depending on the manufacturer, but generally involves heating the carrier oil and adding the CBD extract and other ingredients. The mixture is then stirred and cooled until it solidifies into a salve.
- Step 3- Quality Control: Throughout the manufacturing process, quality control measures are taken to ensure that the final product is safe and effective. This includes testing the CBD extract for purity and potency, as well as testing the final product for contaminants and consistency.
Conclusion
CBD salve is a popular form of topical CBD that can provide targeted relief for pain, inflammation, and other discomforts. The process of making CBD salve involves extracting CBD oil from the hemp plant, selecting other ingredients, and manufacturing the final product. By following strict quality control measures, manufacturers can ensure that their CBD salve is safe and effective for consumers.
Comparison of CBD Salve to other CBD Products - such as CBD oil, capsules, and gummies.
Regular exercise is not only important for cardiovascular health and weight management, but it can also have a positive impact on digestive health. Exercise can help keep the digestive system moving, reduce the risk of constipation, and improve overall gut health.
Here are some of the ways in which exercise can benefit digestive health:
- Promotes regularity: Exercise can help to stimulate the muscles in the digestive tract, promoting regular bowel movements and reducing the risk of constipation.
- Reduces bloating and gas: Exercise can help to reduce bloating and gas by improving digestion and reducing the amount of time food sits in the digestive tract.
- Reduces the risk of colon cancer: Regular exercise has been linked to a reduced risk of colon cancer, possibly due to its ability to promote regularity and reduce inflammation in the gut.
- Boosts gut microbiome: Exercise has been shown to increase the diversity and abundance of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which can improve overall gut health.
So, how much exercise do you need for optimal digestive health? The recommended amount of exercise varies depending on factors such as age, sex, and fitness level, but a general guideline is to aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Examples of moderate-intensity exercise include brisk walking, cycling, swimming, and dancing. However, even light exercise, such as taking a daily walk or doing gentle yoga, can be beneficial for digestive health.
Conclusion
Overall, staying active through regular exercise can have a positive impact on digestive health, promoting regularity, reducing bloating and gas, and improving gut microbiome. So, make sure to incorporate exercise into your daily routine to support a healthy digestive system.
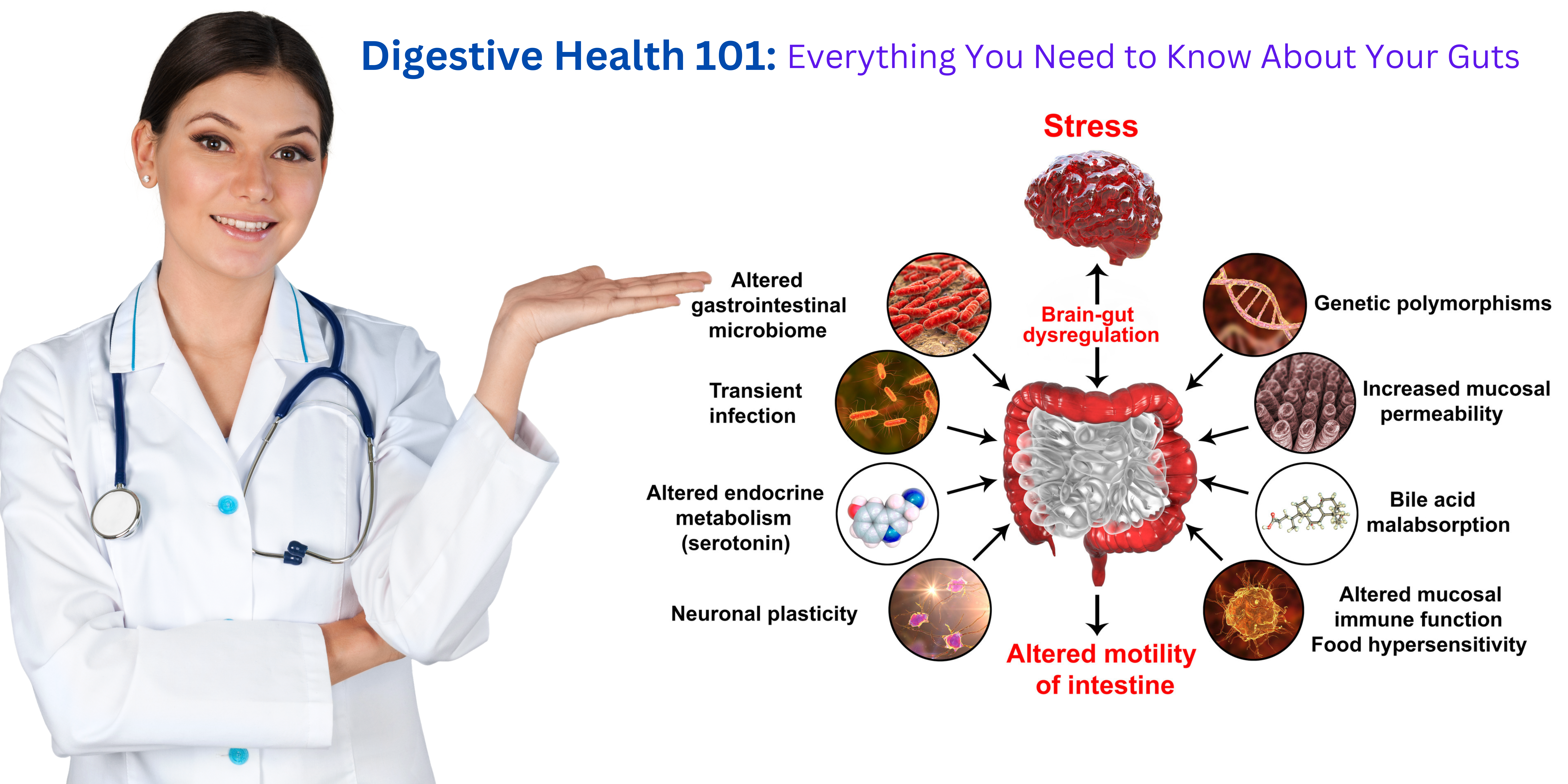
Stress and Digestion: Understanding the Gut-Brain Connection
Have you ever noticed that your stomach feels upset or queasy when you’re stressed or anxious? That’s because there’s a strong connection between the brain and the digestive system, known as the gut-brain axis. When you’re under stress, your body releases hormones that can affect digestion, leading to a range of digestive issues.
Here are some of the ways in which stress can impact digestive health:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Stress is a common trigger for IBS symptoms, such as abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea.
- Heartburn and Acid Reflux: Stress can cause the muscles in the digestive tract to relax, leading to acid reflux and heartburn.
- Constipation and Diarrhea: Stress can affect the movement of food through the digestive tract, leading to constipation or diarrhea.
- Inflammation: Chronic stress can lead to inflammation in the gut, which can contribute to a range of digestive issues, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
So, what can you do to manage stress and support digestive health? Here are some tips:
- Practice stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Exercise regularly to help manage stress and promote healthy digestion.
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet that includes plenty of fiber and probiotics to support gut health.
- Get enough sleep to help reduce stress levels and support overall health.
- Seek professional help if you’re experiencing chronic stress or anxiety.
Common Digestive Issues: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Digestive issues are a common problem that many people experience at some point in their lives. These issues can range from minor discomfort to more serious conditions that require medical treatment. Here are some of the most common digestive issues, along with their causes, symptoms, and treatment options:
- Acid Reflux: Acid reflux occurs when the stomach acid flows back up into the esophagus, causing a burning sensation in the chest or throat. It can be caused by overeating, eating spicy or fatty foods, and lying down immediately after a meal. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, such as avoiding trigger foods and eating smaller, more frequent meals, as well as medications to reduce acid production.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): IBS is a chronic condition that affects the large intestine, causing abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. The exact cause of IBS is unknown, but it may be related to stress, food sensitivities, or an imbalance in the gut microbiome. Treatment options include dietary changes, such as avoiding trigger foods and increasing fiber intake, as well as medications to manage symptoms.
- Constipation: Constipation is a condition in which bowel movements are infrequent or difficult to pass. It can be caused by a lack of fiber in the diet, dehydration, or certain medications. Treatment options include increasing fiber and water intake, as well as over-the-counter laxatives.
- Diarrhea: Diarrhea is a condition in which bowel movements are frequent and loose. It can be caused by a bacterial or viral infection, food intolerances, or certain medications. Treatment options include increasing fluid intake, rest, and over-the-counter medications to manage symptoms.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): IBD is a chronic condition that affects the lining of the digestive tract, causing inflammation and damage. It includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. The exact cause of IBD is unknown, but it may be related to a malfunction of the immune system. Treatment options include medications to reduce inflammation, as well as surgery in more severe cases.
If you’re experiencing digestive issues, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and develop a treatment plan. With the right approach, many digestive issues can be effectively managed and improve your overall quality of life.
Maintaining a Healthy Digestive System: Tips and Strategies for Optimal Digestive Health
Maintaining a healthy digestive system is key to overall health and wellbeing. Here are some tips and strategies for promoting optimal digestive health:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Eating a diet that is high in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and lean protein can help promote healthy digestion. Avoiding processed and high-fat foods can also help prevent digestive issues.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water and fluids is essential for keeping the digestive system functioning properly. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water a day.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular exercise can help improve digestion by promoting movement in the digestive tract and reducing stress.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can have a negative impact on digestion. Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing, can help promote optimal digestive health.
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: Alcohol and caffeine can irritate the digestive tract and lead to digestive issues. Limiting or avoiding these substances can help promote optimal digestive health.
- Get Enough Sleep: Adequate sleep is important for overall health, including digestion. Aim to get at least seven to eight hours of sleep per night.
- Don’t Smoke: Smoking can increase the risk of digestive issues, including acid reflux and stomach ulcers. Quitting smoking can help promote optimal digestive health.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands before eating and after using the bathroom, can help prevent digestive infections.
By following these tips and strategies, you can help promote optimal digestive health and reduce the risk of digestive issues. If you’re experiencing persistent digestive issues, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and develop a treatment plan.
Conclusion: The Importance of Caring for Your Digestive System.
In conclusion, caring for your digestive system is crucial for overall health and wellbeing. Your digestive system plays a vital role in breaking down and absorbing nutrients from the food you eat, and a healthy digestive system can help reduce the risk of a variety of health issues.
By following a balanced diet, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, managing stress, limiting alcohol and caffeine, getting enough sleep, and practicing good hygiene, you can promote optimal digestive health and reduce the risk of digestive issues.
Remember that digestive issues are common and can be caused by a variety of factors, including diet, stress, and underlying medical conditions. If you’re experiencing persistent digestive issues, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and develop a treatment plan.
Taking care of your digestive system may require some effort, but the benefits are well worth it. With a little care and attention, you can keep your digestive system functioning properly and enjoy optimal health and wellbeing.