Welcome to our comprehensive guide on managing type 2 diabetes effectively. In today’s fast-paced world, it has become increasingly important to prioritize our health and well-being.
Type 2 diabetes is a prevalent condition that requires careful management and attention. By understanding the importance of effectively managing type 2 diabetes, we can take control of our health and make positive changes in our lives.
In this article, we will explore practical tips, strategies, and resources to empower you in managing type 2 diabetes. Together, let’s embrace the journey towards optimal health and well-being.
However, managing type 2 diabetes comes with its fair share of challenges. Individuals with type 2 diabetes often face the daunting task of monitoring blood sugar levels, making lifestyle modifications, and adhering to medication regimens. The constant vigilance required can sometimes feel overwhelming.
Nevertheless, it’s important to remember that with the right knowledge, support, and strategies, these challenges can be overcome. In the following sections, we will dive deeper into the practical tips and strategies that can help individuals effectively manage type 2 diabetes and navigate these challenges with confidence. Let’s explore how to conquer the hurdles and embrace a healthier lifestyle.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes: Exploring the Fundamentals of the Condition
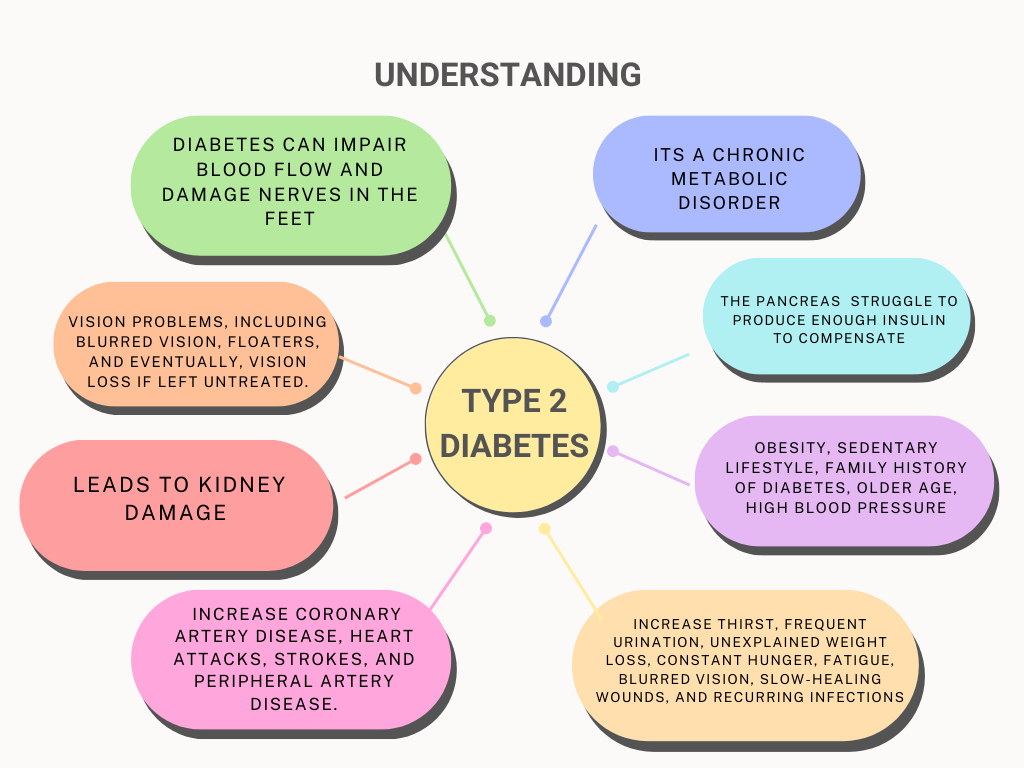
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from insulin resistance. Unlike type 1 diabetes, where the body does not produce insulin, individuals with type 2 diabetes typically produce insulin, but their bodies do not use it effectively. This section will provide a comprehensive overview of type 2 diabetes, including its definition, causes, and underlying mechanisms.
Defining Type 2 Diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes glucose (sugar).
It occurs when the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin or does not produce enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
The result is elevated blood sugar levels, known as hyperglycemia, which can have detrimental effects on various organs and systems in the body.
Causes and Risk Factors
- While the exact cause of type 2 diabetes is not fully understood, several factors contribute to its development:
- Insulin resistance: The body’s cells become resistant to the effects of insulin, leading to impaired glucose uptake.
- Genetic factors: Family history and genetics play a role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to type 2 diabetes.
- Lifestyle factors: Sedentary lifestyle, poor dietary choices, obesity, and excessive abdominal fat increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Age and ethnicity: Advancing age and certain ethnic backgrounds, such as African, Hispanic, Asian, or Pacific Islander descent, are associated with a higher risk.
Underlying Mechanisms
- Insulin and its role in blood sugar regulation:
- Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that allows glucose to enter cells, where it is used for energy.
- In type 2 diabetes, cells become resistant to insulin, leading to impaired glucose uptake and increased blood sugar levels.
Beta-cell dysfunction:
- Beta cells in the pancreas are responsible for producing insulin.
- Over time, these cells may become impaired, resulting in decreased insulin production.
Hormonal imbalances and adipose tissue:
- Adipose tissue, particularly visceral fat, produces hormones and substances that can contribute to insulin resistance and inflammation.
By understanding the basics of type 2 diabetes, including its definition, causes, and underlying mechanisms, individuals can gain insight into the factors influencing their condition. In the following sections, we will explore practical strategies and lifestyle modifications that can effectively manage type 2 diabetes and help individuals lead healthier lives.
Creating a Diabetes Management Plan
Creating a personalized diabetes management plan is crucial in effectively managing Type 2 Diabetes. This plan takes into account your specific needs and circumstances, ensuring that your treatment approach aligns with your goals and lifestyle. Collaborating with healthcare professionals, including doctors, dietitians, and diabetes educators, is instrumental in developing a comprehensive and tailored plan.
When beginning the process of creating a diabetes management plan, it’s important to schedule an appointment with your healthcare team. This team will work closely with you to assess your current health status, understand your medical history, and identify any specific challenges or concerns you may have. They will also consider factors such as your age, weight, activity level, and personal preferences.
Diet is a fundamental component of a diabetes management plan. A registered dietitian can provide expert guidance on creating a balanced meal plan that focuses on controlling blood sugar levels, managing weight, and ensuring proper nutrition. They will help you understand the impact of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats on blood glucose levels and advise on portion sizes, meal timing, and food choices. By following a well-designed meal plan, you can stabilize your blood sugar levels, maintain a healthy weight, and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Exercise is another crucial aspect of diabetes management. Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, manage weight, and enhance cardiovascular health. Your healthcare team, including a physical therapist or exercise specialist, can help you develop an exercise routine that is safe and suitable for your fitness level and overall health. They will consider any physical limitations or complications associated with your diabetes and suggest activities such as walking, swimming, cycling, or strength training. The goal is to incorporate regular exercise into your daily routine and make it an enjoyable and sustainable part of your lifestyle.
Medication plays a significant role in managing Type 2 Diabetes for many individuals. Your healthcare provider will evaluate your specific needs and prescribe appropriate medications to help control blood sugar levels. It’s essential to understand the purpose, dosage, and potential side effects of the prescribed medications. Adhering to the medication regimen as instructed by your healthcare team is vital for maintaining stable blood sugar control. Regular follow-up appointments will allow them to monitor your progress, make any necessary adjustments to your medication plan, and address any concerns or questions you may have.
In addition to diet, exercise, and medication, your diabetes management plan may also include self-monitoring of blood sugar levels. This involves checking your blood glucose levels regularly using a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring system. Self-monitoring allows you to track your progress, identify patterns, and make adjustments to your treatment plan as needed. Your healthcare team will guide you on how often to check your blood sugar levels and what target ranges to aim for.
Remember, your diabetes management plan is not static. It will evolve and adapt over time as your needs and circumstances change. Regular communication with your healthcare team is essential to ensure that your plan remains effective and aligned with your goals. Be proactive in discussing any challenges, successes, or concerns you encounter along the way.
By collaborating with healthcare professionals and actively participating in the creation of your diabetes management plan, you are taking a proactive and empowering approach to managing Type 2 Diabetes. With their guidance and your commitment, you can achieve optimal blood sugar control, reduce the risk of complications, and improve your overall quality of life.
Healthy Eating for Diabetes Management
Maintaining a healthy and balanced diet is essential for effectively managing blood sugar levels and overall diabetes management. When it comes to healthy eating for diabetes, there are several key principles to keep in mind.
- Focus on Nutrient-Dense Foods: Opt for nutrient-dense foods that provide a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and fiber while being relatively low in calories. These include whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Nutrient-dense foods help support overall health and provide sustained energy throughout the day.
- Control Portion Sizes: Portion control is crucial for managing blood sugar levels and maintaining a healthy weight. Be mindful of the quantity of food you consume and avoid oversized portions. Using smaller plates and bowls can help control portion sizes visually. Additionally, listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues to avoid overeating.
- Emphasize Whole Grains: Whole grains are an excellent choice for individuals with Type 2 Diabetes as they are rich in fiber, which helps regulate blood sugar levels. Whole grain options include whole wheat, brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole grain bread and pasta. These provide more nutrients and have a lower glycemic index compared to refined grains.
- Choose Lean Proteins: Incorporating lean proteins into your meals helps maintain muscle mass, promote satiety, and stabilize blood sugar levels. Good sources of lean protein include skinless poultry, fish, tofu, legumes, and low-fat dairy products. Avoid high-fat cuts of meat and processed meats, as they can be high in unhealthy saturated and trans fats.
Include Plenty of Fruits and Vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, making them an essential part of a diabetes-friendly diet. They are generally low in calories and have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. Aim to include a variety of colorful fruits and non-starchy vegetables in your meals and snacks.
Be Mindful of Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels. Understanding how different types of carbohydrates affect your blood sugar is crucial for proper diabetes management. Focus on consuming complex carbohydrates from whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, as they are digested more slowly and have a smaller impact on blood sugar levels compared to refined carbohydrates like white bread, sugary beverages, and sweets.
Monitor Added Sugars: Be mindful of foods and beverages with added sugars, as they can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. Limit or avoid sugary drinks, sweets, desserts, and processed snacks. Instead, choose natural sources of sweetness like fresh fruits or small amounts of natural sweeteners like stevia or monk fruit.
Incorporate Healthy Fats: Including healthy fats in your diet can help improve insulin sensitivity and promote heart health. Opt for unsaturated fats found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon. Limit saturated and trans fats found in fried foods, high-fat dairy products, and fatty cuts of meat.
Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration is essential for overall health and blood sugar management. Drink plenty of water throughout the day and limit sugary beverages. Avoid excessive alcohol consumption, as it can interfere with blood sugar control and contribute to weight gain.
Remember, everyone’s nutritional needs may vary, and it is crucial to work with a registered dietitian who specializes in diabetes to develop a personalized meal plan that suits your specific needs and goals. They can provide individualized guidance, help you understand how different foods impact your blood sugar levels, and offer strategies to make healthy eating enjoyable and sustainable.
By adopting a balanced and diabetes-friendly diet, you can support stable blood sugar levels, achieve a healthy weight, and reduce the risk of complications associated with Type 2 Diabetes. Combined with other elements of diabetes management, such as regular exercise and medication adherence, healthy eating plays a vital role in maintaining optimal health and well-being.
Incorporating Physical Activity
Incorporating regular physical activity into your lifestyle is an essential component of managing Type 2 Diabetes.
Engaging in exercises such as walking, swimming, cycling, or strength training offers numerous benefits that contribute to improved overall health and blood sugar control. By creating an exercise routine and overcoming common barriers, you can ensure consistency and maximize the positive impact of physical activity.
- Understand the Benefits: Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, which allows your cells to better utilize glucose and leads to improved blood sugar control. It can also contribute to weight management by burning calories and building lean muscle mass. Additionally, exercise helps lower blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, reduce the risk of heart disease, and enhance overall cardiovascular health.
- Choose Activities You Enjoy: Find physical activities that you genuinely enjoy, as this increases the likelihood of sticking with them long-term. Whether it’s brisk walking, dancing, swimming, cycling, yoga, or a sport you love, engaging in activities that bring you joy will make exercise a more enjoyable part of your routine.
- Set Realistic Goals: Start by setting realistic and achievable goals for your physical activity. Gradually increase the duration and intensity of your workouts over time. For example, aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity spread throughout the week, such as brisk walking for 30 minutes a day, five days a week. You can also include strength training exercises two or more days a week to build muscle and improve overall strength.
- Incorporate Exercise into Daily Life: Look for opportunities to incorporate physical activity into your daily routine. Take the stairs instead of the elevator, walk or bike to nearby destinations instead of driving, or take short breaks during work to stretch or take a quick walk. These small lifestyle changes can add up and contribute to your overall physical activity level.
- Overcome Barriers: Identify and address any barriers that may prevent you from being physically active. Common barriers include lack of time, fatigue, and self-consciousness. Find strategies to overcome these barriers, such as scheduling specific times for exercise, breaking workouts into shorter sessions throughout the day, inviting a friend or family member to join you, or finding alternative ways to be active when weather conditions are unfavorable.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: It’s important to monitor your blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise, especially when starting a new exercise routine or making significant changes to your current regimen. This will help you understand how your body responds to physical activity and make any necessary adjustments to your diabetes management plan.
- Stay Hydrated: Hydration is crucial during physical activity, as it helps maintain optimal bodily functions and prevents dehydration. Drink water before, during, and after exercise to stay properly hydrated. Avoid sugary sports drinks unless advised by your healthcare team.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how your body feels during exercise. If you experience any discomfort, dizziness, or shortness of breath, it’s important to stop and consult with your healthcare team. They can help you determine if any adjustments to your exercise routine or diabetes management plan are necessary.
- Seek Support and Accountability: Consider finding an exercise buddy or joining a group or class that focuses on physical activity for individuals with diabetes. This can provide a sense of community, support, and accountability, making it easier to stay motivated and committed to your exercise goals.
Remember, it’s always essential to consult with your healthcare team before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or concerns. They can provide personalized guidance based on your individual needs and help ensure that your exercise routine is safe and beneficial for your overall diabetes management. With consistency and commitment, incorporating regular physical activity into your daily life can significantly improve your diabetes management and overall well-being.
Medications and Insulin Management
Medications and insulin are important tools in managing Type 2 Diabetes, especially when lifestyle modifications alone are not sufficient to achieve target blood sugar levels. Understanding the medications prescribed, their mechanisms of action, and potential side effects is crucial for effective diabetes management. Adhering to the prescribed treatment plan, monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, and making any necessary adjustments in consultation with healthcare professionals ensures optimal management of the condition.
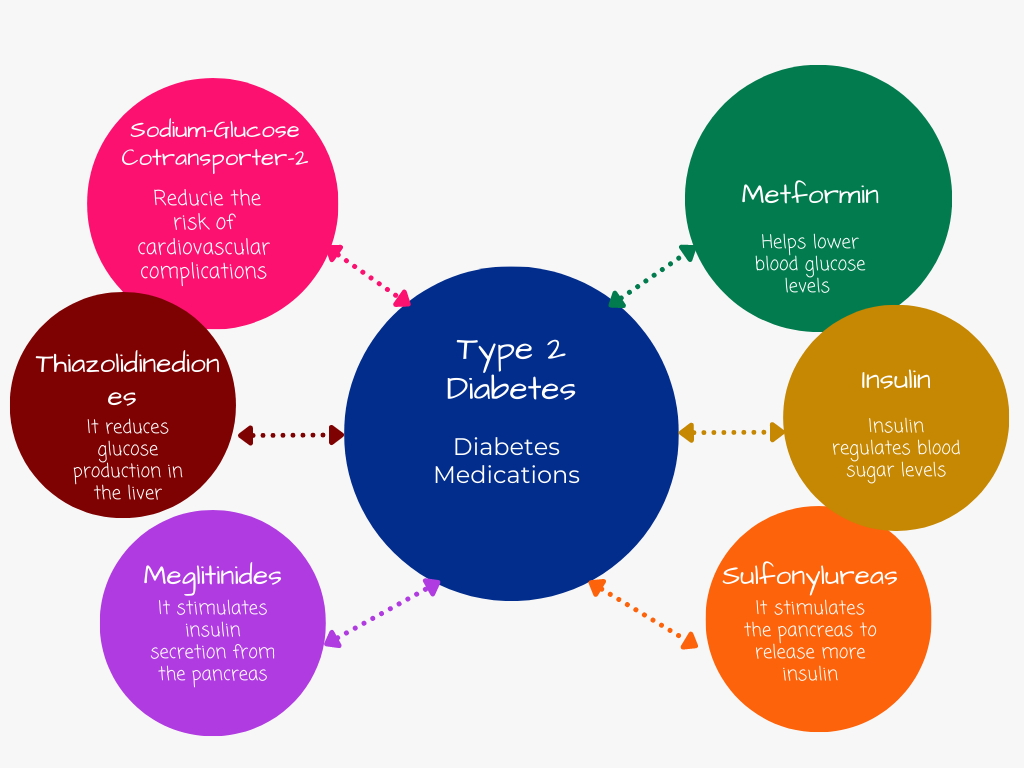
1.Oral Medications: Several classes of oral medications are commonly used to manage Type 2 Diabetes. These medications work in different ways to help control blood sugar levels:
a. Metformin: Metformin is usually the first-line medication prescribed for Type 2 Diabetes. It helps reduce glucose production in the liver, improve insulin sensitivity, and enhance glucose uptake by muscle cells.
b. Sulfonylureas: Sulfonylureas stimulate the release of insulin from the pancreas and help lower blood sugar levels. They are typically taken once or twice a day.
c. Thiazolidinediones: Thiazolidinediones improve insulin sensitivity and help lower blood sugar levels. They are taken once a day.
d. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors: DPP-4 inhibitors help lower blood sugar by increasing the release of insulin and reducing the production of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar levels.
e. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors: SGLT-2 inhibitors work by blocking the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys, leading to increased glucose excretion in the urine.
f. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors: Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates in the intestine, thereby reducing post-meal blood sugar spikes.
2.Injectable Medications: In addition to oral medications, there are injectable medications that can be used to manage Type 2 Diabetes:
a. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists: GLP-1 receptor agonists stimulate insulin secretion, suppress glucagon release, slow down digestion, and promote satiety. They are typically injected once a day or once a week.
b. Amylin analogs: Amylin analogs mimic the hormone amylin, which helps regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down gastric emptying, suppressing glucagon release, and increasing satiety. They are typically injected before meals.
3.Insulin Therapy: For some individuals with Type 2 Diabetes, insulin therapy may be necessary to achieve optimal blood sugar control. Insulin is injected using a syringe, pen, or insulin pump. Different types of insulin are available, including:
a. Rapid-acting insulin: Rapid-acting insulin starts working within 15 minutes after injection, peaks within 1 to 2 hours, and lasts for about 3 to 4 hours. It is usually taken before meals to manage post-meal blood sugar spikes.
b. Short-acting insulin: Short-acting insulin begins working within 30 minutes after injection, peaks within 2 to 3 hours, and lasts for about 4 to 6 hours. It is usually taken before meals to control blood sugar levels.
c. Intermediate-acting insulin: Intermediate-acting insulin starts working within 2 to 4 hours after injection, peaks within 4 to 12 hours, and lasts for about 12 to 18 hours. It helps manage blood sugar levels between meals and overnight.
d. Long-acting insulin: Long-acting insulin provides a steady release of insulin over an extended period, usually 24 hours. It helps maintain basal insulin levels and provides background insulin coverage.
4.Adherence to Medications: It is crucial to follow the prescribed treatment plan and take medications as directed by your healthcare provider. Skipping doses or discontinuing medications without medical advice can negatively impact blood sugar control. If you have concerns about your medications or experience side effects, discuss them with your healthcare team to explore alternative options.
5.Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of your medication regimen and making any necessary adjustments. Your healthcare provider will guide you on how often to check your blood sugar and what target ranges to aim for.
6.Consultation with Healthcare Professionals: It’s important to maintain open communication with your healthcare team, including your primary care physician, endocrinologist, or diabetes educator. Regular follow-up visits will allow for the review of your treatment plan, medication effectiveness, and potential adjustments to achieve optimal blood sugar control.
7.Education and Self-Management: Educate yourself about your medications, their mechanisms of action, and potential side effects. Understand the importance of proper injection techniques, if applicable, and storage requirements. Develop good self-management habits, such as tracking blood sugar levels, recording medication doses, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Managing Type 2 Diabetes involves a multifaceted approach, and medications, along with lifestyle changes, play a significant role. By understanding your medications, following your treatment plan, and collaborating with your healthcare team, you can effectively manage your blood sugar levels and minimize the risk of complications associated with diabetes. Remember to always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and support.
Stress Management and Emotional Well-being
Stress is a common and often unavoidable part of life, but for individuals with Type 2 Diabetes, managing stress is particularly important. Stress can have a direct impact on blood sugar levels, making it crucial to employ effective stress management techniques to mitigate its negative effects. Prioritizing emotional well-being through self-care and seeking support when needed is essential for managing Type 2 Diabetes effectively.
- Understand the Connection: Stress triggers the release of hormones that can cause blood sugar levels to rise. This is because stress activates the body’s “fight-or-flight” response, which releases stored glucose into the bloodstream for immediate energy. For individuals with diabetes, this can disrupt blood sugar control and lead to fluctuations in glucose levels.
- Practice Mindfulness: Mindfulness is the practice of being fully present in the moment, without judgment. It involves focusing on your thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations. Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help reduce stress and promote emotional well-being. Consider incorporating mindfulness into your daily routine, even if it’s just for a few minutes each day.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing exercises are a simple yet effective way to manage stress. They help activate the body’s relaxation response, which counteracts the physiological effects of stress. Practice diaphragmatic breathing by inhaling deeply through your nose, allowing your abdomen to rise, and exhaling slowly through your mouth. Repeat this for several cycles to promote a sense of calm and relaxation.
- Engage in Activities that Bring Joy: Engaging in activities that you enjoy can help reduce stress and promote emotional well-being. Find hobbies, such as reading, gardening, painting, or listening to music, that bring you joy and make time for them regularly. Engaging in activities that you find pleasurable can help distract from stressors and improve your overall mood.
- Prioritize Self-Care: Self-care is essential for managing stress and maintaining emotional well-being. Make time for activities that nourish your mind, body, and soul. This can include getting enough sleep, eating nutritious meals, exercising regularly, and engaging in relaxation techniques, such as taking warm baths or practicing yoga. Taking care of yourself physically and emotionally can help build resilience to stress.
- Seek Support: It’s important to remember that you don’t have to manage diabetes-related stress alone. Reach out to your support network, including family, friends, or a support group, to share your feelings and concerns. Talking to others who understand your experience can provide comfort and valuable insights. Additionally, consider working with a mental health professional who can provide guidance and support in managing stress and improving emotional well-being.
- Set Realistic Expectations: Managing stress involves setting realistic expectations for yourself. Recognize that you cannot control everything and that it’s okay to ask for help when needed. Set priorities, delegate tasks when possible, and practice self-compassion. Be kind to yourself and acknowledge that managing diabetes can be challenging, but you are doing your best.
- Time Management and Organization: Effective time management and organization can help reduce stress by creating structure and reducing the feeling of being overwhelmed. Use tools such as calendars, to-do lists, or smartphone apps to manage tasks and appointments. Break tasks into smaller, manageable steps, and prioritize them based on importance. This can help create a sense of control and reduce stress associated with deadlines and time constraints.
- Monitor Your Emotional Well-being: Regularly check in with your emotional well-being and be aware of signs of stress or burnout. If you notice persistent feelings of anxiety, sadness, or hopelessness, or if you are having difficulty managing your stress levels, seek professional help. A mental health professional can provide guidance, support, and strategies to manage stress and improve your overall emotional well-being.
Managing stress and prioritizing emotional well-being is an important aspect of managing Type 2 Diabetes. By incorporating stress management techniques, practicing self-care, seeking support when needed, and maintaining a positive mindset, you can effectively cope with the challenges of diabetes and promote your overall well-being. Remember, it’s a journey, and small steps toward managing stress can make a significant difference in your diabetes management and quality of life.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a crucial component of managing Type 2 Diabetes. Regular monitoring provides valuable information about how well your diabetes management plan is working, allowing you to make necessary adjustments and maintain optimal blood sugar control. There are different methods of monitoring blood sugar levels, each offering unique benefits and insights into your glucose levels.
1.Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG): Self-monitoring of blood glucose involves using a glucose meter to check your blood sugar levels at home. This method allows you to obtain immediate results and make real-time adjustments to your management plan. Here’s how it works:
a. Target Blood Sugar Ranges: Work with your healthcare team to establish target blood sugar ranges for fasting (before meals) and postprandial (after meals) levels. These ranges help guide your management decisions and indicate whether your blood sugar levels are within the desired range. b. Frequency of Testing: Your healthcare provider will determine how often you should test your blood sugar levels based on factors such as your treatment plan, medication regimen, and individual needs. Initially, frequent testing may be necessary to understand your body’s response to different foods, activities, and medications.
c. Interpreting Results: When monitoring your blood sugar levels, it’s important to understand the numbers and their implications. Aim for blood sugar levels within the target range established by your healthcare provider. Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) and high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) can have adverse effects on your health and require appropriate management.
d. Making Adjustments: If your blood sugar levels consistently fall outside the target range, it may be necessary to make adjustments to your diabetes management plan. This can include modifying your diet, exercise routine, medication dosage, or timing. Consult your healthcare team for guidance and support in making these adjustments.
2.Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): CGM is a technology that provides continuous information about your glucose levels throughout the day and night. It involves wearing a sensor under the skin that measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. CGM offers several benefits:
a. Real-time Data: CGM provides real-time information about your glucose levels, including trends and patterns. This can help you understand how different factors, such as meals, exercise, and stress, affect your blood sugar levels.
b. Alerts and Alarms: CGM systems can alert you when your glucose levels are too high or too low, helping you take immediate action to prevent complications. These alerts can be particularly beneficial during sleep or when you may not notice symptoms of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
c. Data Analysis: CGM systems provide data reports that can be reviewed by you and your healthcare team. These reports help identify patterns, evaluate the effectiveness of your management plan, and make informed decisions about adjustments.
d. Treatment Optimization: CGM can assist in fine-tuning your diabetes management plan by providing detailed insights into your glucose levels. It can help you identify problem areas and make targeted adjustments to improve your blood sugar control.
3.A1C Test: The A1C test measures your average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. It provides a snapshot of your overall glucose control and is typically performed during routine check-ups or as recommended by your healthcare provider. Here’s what you need to know:
a. Target A1C Level: The target A1C level may vary depending on individual factors, such as age, health status, and the presence of other medical conditions. Generally, a target A1C level of below 7% is recommended for most people with Type 2 Diabetes.
b. Frequency of Testing: The frequency of A1C testing depends on your overall diabetes management and how well your blood sugar levels are controlled. It is typically done every three to six months, but your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate interval for you.
c. Interpreting Results: The A1C test provides an average of your blood sugar levels over time. Lower A1C levels indicate better glucose control, while higher levels may suggest the need for adjustments to your management plan.
d. Adjusting the Management Plan: If your A1C levels are consistently above the target range, your healthcare provider may recommend modifications to your diabetes management plan. This may involve changes in diet, exercise, medication, or other interventions to help achieve better blood sugar control.
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels empowers you to take an active role in managing your diabetes. By understanding the target ranges, interpreting the results, and making necessary adjustments to your management plan, you can maintain optimal blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications associated with Type 2 Diabetes. Work closely with your healthcare team to develop a monitoring routine that suits your needs and supports your overall diabetes management goals.
Preventing Diabetes Complications
Preventing complications associated with Type 2 Diabetes is crucial for maintaining long-term health and well-being. By effectively managing blood sugar levels, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and attending regular check-ups and screenings, individuals can reduce the risk of complications or detect them early when treatment is most effective. Here are some key preventive measures to consider:
- Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining optimal blood sugar control is the cornerstone of preventing diabetes complications. Consistently monitoring your blood sugar levels, following your diabetes management plan, taking medications as prescribed, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments are essential. Aim to keep your blood sugar levels within the target range established by your healthcare provider.
- Healthy Eating: Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet is vital in preventing complications. Focus on consuming a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Limit the intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-sodium foods. Work with a registered dietitian to develop a personalized meal plan that suits your specific dietary needs and goals.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity offers numerous health benefits and helps prevent complications. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, each week. Additionally, incorporate strength training exercises to improve muscle strength and enhance overall fitness. Consult with your healthcare team before starting any exercise program to ensure it is safe and suitable for you.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is important for preventing diabetes complications. If you are overweight or obese, losing even a modest amount of weight can significantly improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of complications. Adopt a gradual and sustainable weight loss approach by combining a balanced diet with regular physical activity.
- Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Control: High blood pressure and elevated cholesterol levels are common comorbidities of Type 2 Diabetes and can increase the risk of complications. Monitor your blood pressure regularly, and if it is elevated, work with your healthcare provider to develop a management plan that may include lifestyle changes and medications. Similarly, manage your cholesterol levels by following a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and taking prescribed medications if necessary.
- Regular Check-ups and Screenings: Attend regular check-ups and screenings as recommended by your healthcare provider. These appointments allow for the monitoring of your overall health, detection of any potential complications, and adjustment of your management plan if needed. Regular screenings for conditions such as eye disease, kidney function, nerve damage, and cardiovascular health are crucial for early detection and intervention.
- Foot Care: Individuals with diabetes are at an increased risk of foot complications. Practice good foot care by inspecting your feet daily for any cuts, sores, or signs of infection. Keep your feet clean and moisturized, wear properly fitting shoes, and avoid going barefoot. Regularly visit a podiatrist for foot exams and seek prompt medical attention for any foot-related concerns.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can impact blood sugar control and increase the risk of complications. Employ stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, and engaging in activities that promote relaxation. Prioritize self-care, seek support when needed, and incorporate stress-reducing practices into your daily routine.
- Smoking Cessation: If you smoke, quitting is essential for preventing diabetes-related complications. Smoking increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health problems. Seek professional help, join support groups, or explore smoking cessation programs to assist you in your journey to quit smoking.
- Emotional Well-being: Prioritize your emotional well-being and seek support when needed. Living with diabetes can be challenging, and addressing the emotional aspects of the condition is vital. Engage in activities that bring you joy and relaxation, practice self-care, and consider joining support groups or seeking professional counseling to help cope with any emotional challenges.
By implementing these preventive measures and maintaining good overall health, you can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with Type 2 Diabetes. Remember to work closely with your healthcare team, stay informed about your condition, and take proactive steps to preserve your long-term health and well-being.
Support Systems and Resources
Building a strong support system and utilizing available resources are key factors in effectively managing Type 2 Diabetes. Here’s how you can harness support systems and utilize various resources to enhance your diabetes management:
- Family and Friends: Share your journey with your loved ones and educate them about Type 2 Diabetes. Seek their understanding, support, and encouragement as you navigate the challenges of managing the condition. They can play an essential role in helping you maintain a healthy lifestyle, reminding you to take medications, and providing emotional support.
- Diabetes Support Groups: Joining local or online diabetes support groups can connect you with individuals who understand the daily realities of living with diabetes. These groups provide a platform for sharing experiences, discussing challenges, and learning from one another. It can be empowering to connect with others who face similar struggles and triumphs, offering a sense of camaraderie and encouragement.
- Healthcare Team: Your healthcare team, including doctors, nurses, dietitians, and diabetes educators, is a valuable resource. Establish open communication with your healthcare providers, ask questions, seek clarification, and actively participate in your treatment plan. They can provide personalized guidance, offer education, and help you make informed decisions about your diabetes management.
- Online Resources: The internet offers a wealth of information and resources for individuals with Type 2 Diabetes. Reliable websites, such as those run by diabetes organizations, provide educational materials, tips for managing diabetes, and updates on the latest research and treatment options. Be discerning when seeking information online, and rely on reputable sources.
- Mobile Applications: There are numerous mobile applications available that can assist in diabetes management. These apps often provide features such as blood sugar tracking, meal planning, medication reminders, and exercise tracking. Some even offer educational resources and allow you to connect with online communities of individuals managing diabetes. Explore different apps and choose ones that align with your specific needs and preferences.
- Diabetes Education Programs: Diabetes education programs, often offered by hospitals or community centers, provide comprehensive information and skills to effectively manage Type 2 Diabetes. These programs cover topics such as healthy eating, physical activity, medication management, and blood sugar monitoring. Participating in such programs can empower you with knowledge and practical skills to navigate your diabetes journey confidently.
- Social Media Communities: Social media platforms host various communities focused on diabetes management. Joining relevant groups or following reputable accounts can provide a supportive online community where you can connect with others, share experiences, learn from tips and success stories, and stay updated on the latest developments in diabetes management.
- National Diabetes Organizations: National diabetes organizations, such as the American Diabetes Association or Diabetes UK, offer a wealth of resources and support. They provide educational materials, organize events, offer helplines, and advocate for diabetes awareness and improved care. These organizations can serve as valuable sources of information and support.
By tapping into support systems and utilizing available resources, you can enhance your diabetes management journey. Remember to engage with your support network, stay informed through trusted sources, and leverage technology to optimize your diabetes management practices. Together, these resources can provide you with the knowledge, motivation, and encouragement needed to navigate Type 2 Diabetes successfully.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing Type 2 Diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses various aspects of your life. By creating a personalized diabetes management plan, adopting a healthy eating pattern, incorporating regular physical activity, understanding medications and insulin management, practicing stress management techniques, monitoring blood sugar levels, preventing complications, utilizing support systems and resources, and prioritizing your emotional well-being, you can successfully navigate the challenges of living with diabetes.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Reach out to your healthcare team, lean on the support of loved ones, join diabetes support groups, and leverage the wealth of information and tools available online and through mobile applications. By actively engaging in your diabetes management and making empowered decisions, you can lead a fulfilling life while effectively managing Type 2 Diabetes.
Take charge of your health, stay committed to your well-being, and remember that small steps towards positive change can lead to significant improvements in your overall health and quality of life. With determination, perseverance, and the right support, you have the power to thrive with Type 2 Diabetes.
SugarMute Reviews 2025: Does It Really Work? Ingredients & Side Effects
SugarMute Reviews 2025: Complete Analysis & Real User Results By William Smith, Certified Dietician & Health Enthusiast (15+ Years Experience) ★★★★☆ 4.2/5 Based on Real
Ozelyt CS 20b Reviews: Does It Really Work? Side Effects & Ingredients Analysis 2025
Ozelyt CS 20b Reviews: Complete Analysis & My Professional Opinion By William Smith – Certified Dietician with 15+ Years Experience Health & Wellness Specialist |