BeVital Slim PM Reviews 2025: Is This Bedtime Fat Burner the Real Deal?
If you’ve ever tried to lose weight but felt sabotaged by cravings, stress, or poor sleep, you’re not alone. Hormonal weight gain – especially belly
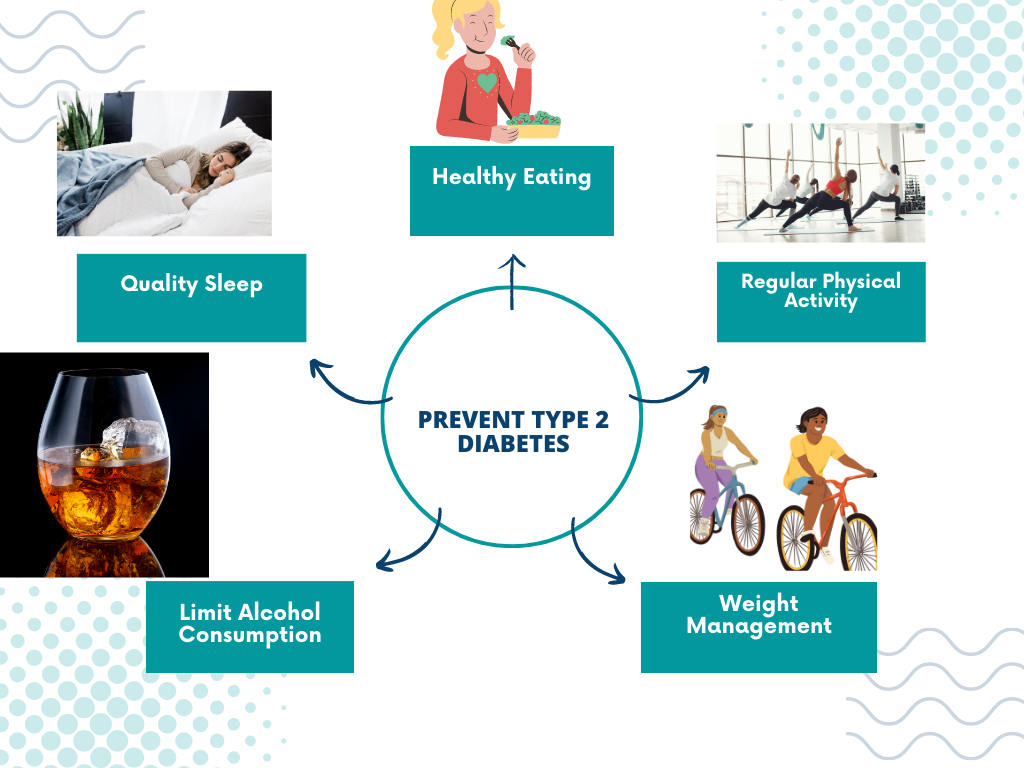
In a world where chronic diseases are on the rise, taking charge of your health has never been more important. Among these diseases, type 2 diabetes stands as a significant concern due to its increasing prevalence and adverse health implications. However, the good news is that type 2 diabetes is largely preventable through proactive measures and the adoption of healthy lifestyle changes and habits. By making conscious choices in our daily lives, we can significantly reduce the risk of developing this condition and pave the way for a healthier future.
The significance of lifestyle changes and habits cannot be overstated when it comes to preventing type 2 diabetes. Research has shown that a substantial portion of type 2 diabetes cases can be attributed to modifiable risk factors, such as poor dietary choices, sedentary behavior, excess weight, and unhealthy habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. By addressing these factors head-on and making positive changes, we can greatly influence our susceptibility to the disease.
This article aims to provide you with a comprehensive guide on how to prevent type 2 diabetes through key lifestyle changes and habits. We will explore the importance of healthy eating, regular physical activity, weight management, stress management, quality sleep, and the impact of smoking and alcohol. Additionally, we will discuss the significance of regular health screenings and check-ups in detecting and managing risk factors. By empowering ourselves with knowledge and implementing these essential lifestyle modifications, we can take control of our health and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Let’s embark on this journey together and pave the way for a diabetes-free future.
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from either insulin resistance or insufficient insulin production. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels. It facilitates the transport of glucose from the bloodstream into cells, where it is used as a source of energy. In individuals with type 2 diabetes, cells become resistant to the effects of insulin, leading to an impaired glucose uptake and accumulation of sugar in the blood.
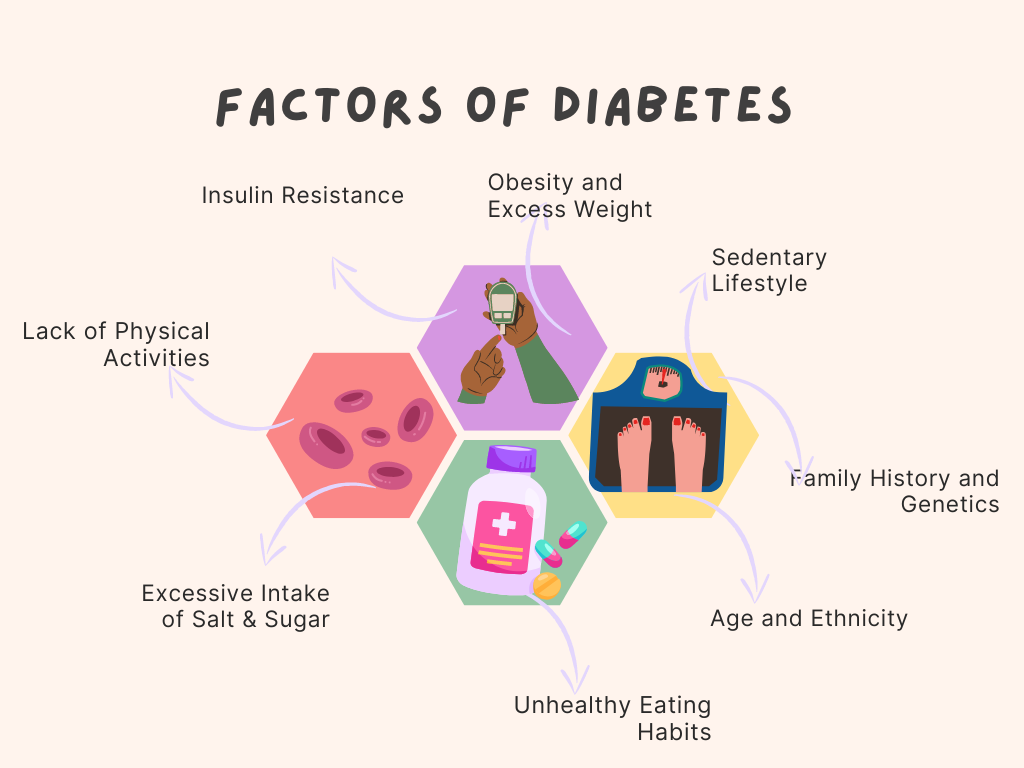
Several risk factors contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. One of the most significant factors is obesity, as excess body fat can interfere with the body’s ability to utilize insulin effectively. A sedentary lifestyle, characterized by a lack of physical activity, further exacerbates the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Family history also plays a role, as individuals with close relatives who have the condition are more likely to develop it themselves. Age is another factor, with the risk of type 2 diabetes increasing as individuals grow older.
Finally, certain ethnicities, such as African Americans, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Asians, have a higher predisposition to type 2 diabetes.
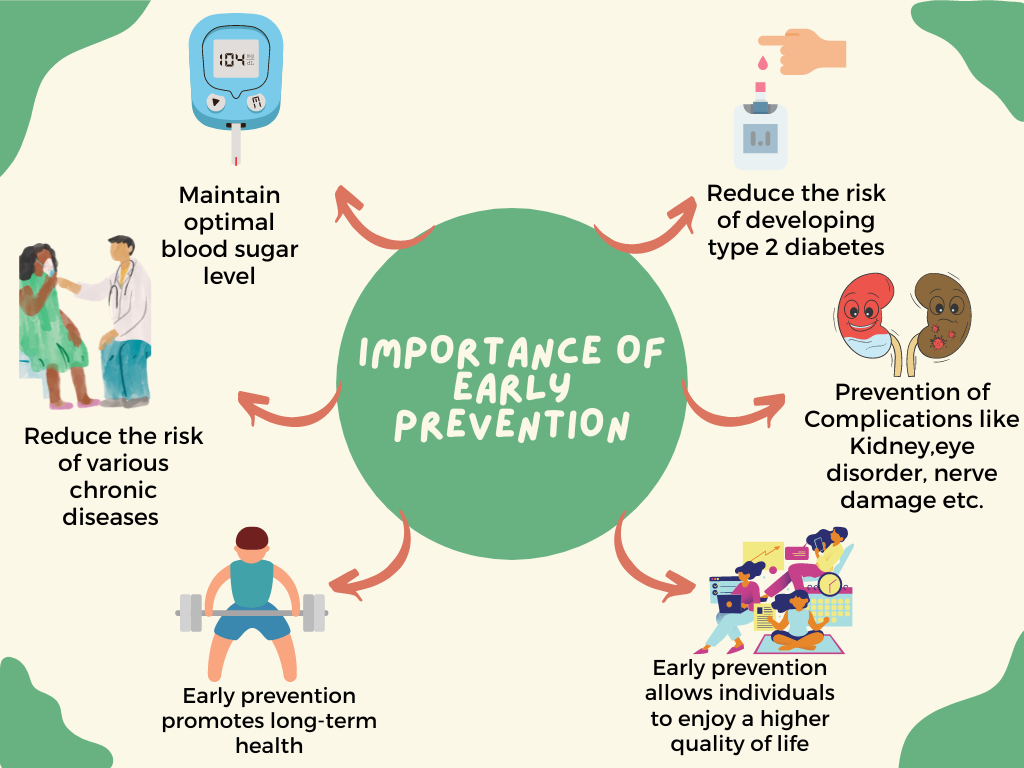
Early prevention is of paramount importance when it comes to managing and reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. By recognizing the early signs and risk factors, individuals have the opportunity to take proactive steps towards safeguarding their health. Engaging in preventive measures, such as adopting a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and weight management, can have a profound impact on preventing or delaying the onset of type 2 diabetes.
Additionally, early detection through regular health screenings and check-ups allows for timely intervention and management of risk factors. By addressing the condition in its early stages, individuals can avoid or minimize the potential complications associated with type 2 diabetes, including cardiovascular disease, kidney problems, nerve damage, and vision loss.
Moreover, early prevention not only benefits individuals on a personal level but also has broader societal implications by reducing the burden on healthcare systems. Emphasizing the importance of early prevention empowers individuals to take control of their health and make informed choices that can positively impact their well-being and quality of life.
Diet plays a crucial role in preventing type 2 diabetes. The food choices we make can have a significant impact on our overall health and well-being. By making smart decisions about what we eat, we can significantly reduce our risk of developing this chronic condition. A balanced and nutritious diet is paramount in diabetes prevention, as it ensures the intake of essential nutrients while limiting the consumption of foods that can contribute to insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar levels. Through mindful eating and incorporating key food groups, we can take proactive steps towards a healthier future.
Maintaining a balanced diet is of utmost importance when it comes to preventing type 2 diabetes and promoting overall health. A balanced diet ensures that our bodies receive the necessary nutrients in the right proportions. It provides the foundation for optimal functioning, including regulating blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy weight, and supporting proper insulin function. A well-balanced diet consists of a variety of nutrient-dense foods from different food groups, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants that are crucial for maintaining a healthy body and reducing the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes. By focusing on a balanced diet, we can nourish our bodies, support metabolic health, and make positive strides towards diabetes prevention. It’s important to note that a balanced diet is not about strict restrictions or deprivation but rather about making sustainable and mindful choices that support long-term well-being.
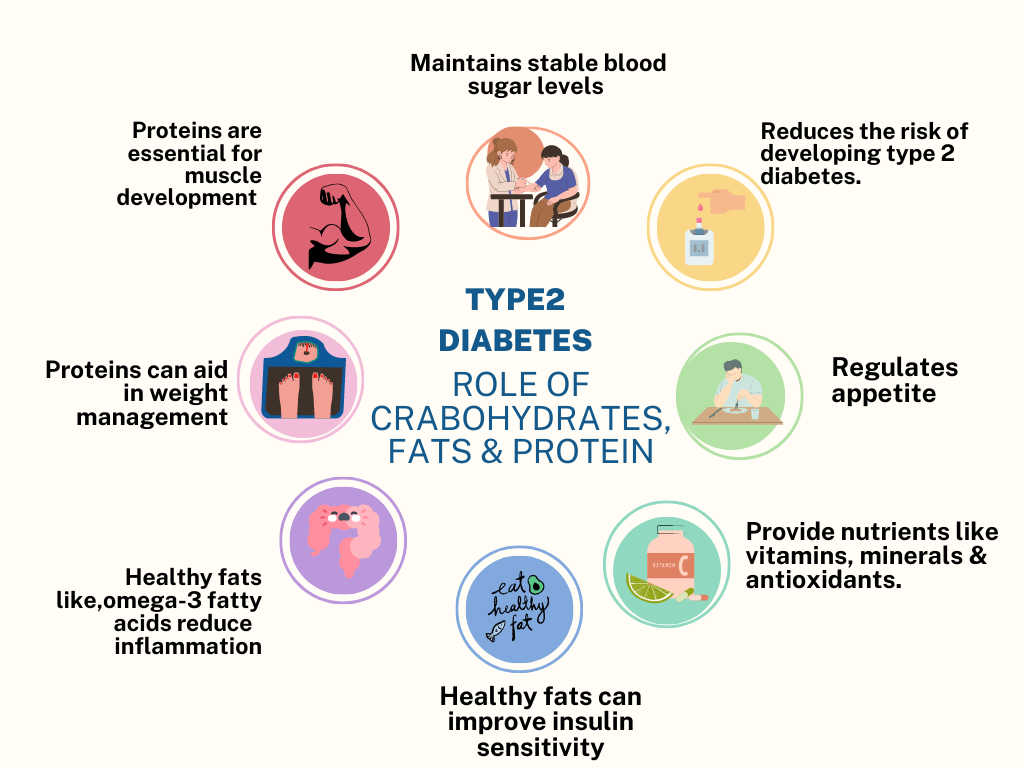
Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins all play specific roles in preventing diabetes. Understanding their impact and making smart choices within each category can contribute to a balanced and diabetes-preventive diet.
Overall, a balanced diet that includes the right types and amounts of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins is key in preventing diabetes. Focus on incorporating whole foods, prioritize complex carbohydrates, choose healthy fats, and opt for lean sources of protein. Moderation and balance are crucial when it comes to macronutrient intake. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance on appropriate portion sizes and specific dietary needs to support diabetes prevention.
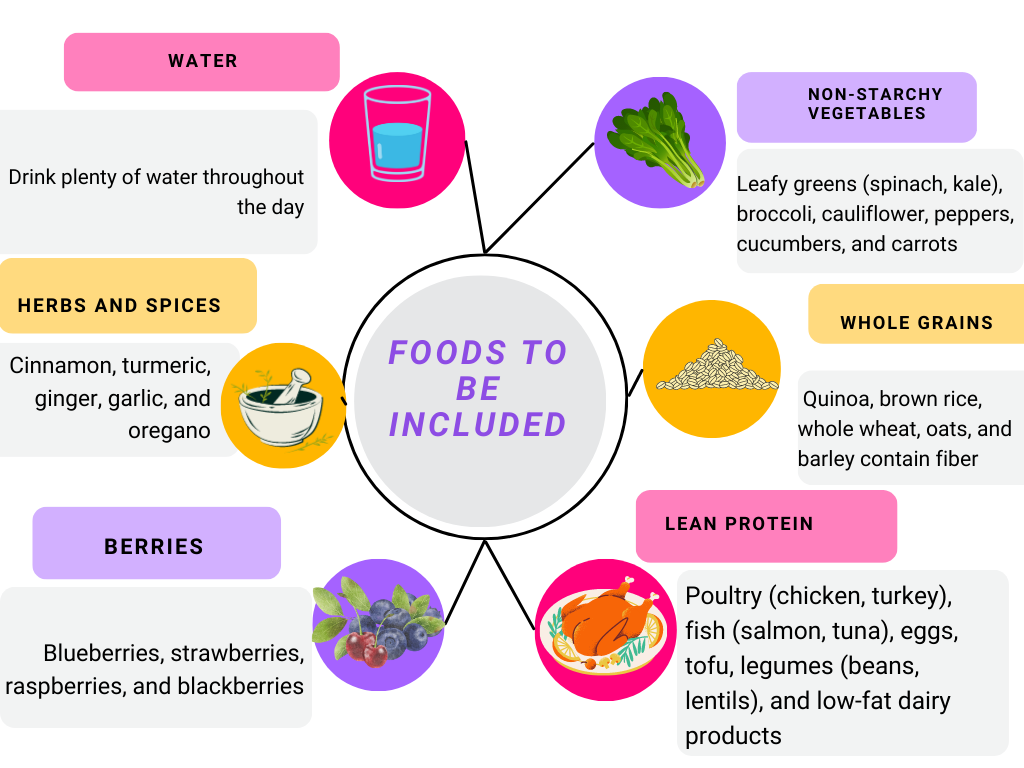
Including certain foods in your diet can play a significant role in preventing diabetes. Here are some key foods to consider incorporating:
Remember, a balanced and varied diet is essential for overall health and diabetes prevention. Focus on portion control, mindful eating, and maintaining a healthy weight alongside these food choices. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance and help you tailor your diet to meet your specific needs and goals.
While incorporating healthy foods is important for diabetes prevention, it’s equally crucial to be aware of foods that should be avoided or limited. Here are some foods to be cautious about:
By being mindful of these food choices and making healthier alternatives, you can reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and promote overall well-being. Remember, moderation is key, and it’s important to find a balance that suits your individual needs and preferences. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance based on your specific circumstances.
Meal planning and portion control are effective strategies for maintaining a healthy diet and preventing type 2 diabetes. Here are some practical tips to help you with meal planning and portion control:
Remember, meal planning and portion control are lifestyle habits that take time to develop. Be patient with yourself and focus on making gradual changes. With consistency and practice, you can successfully adopt these habits and support your journey towards preventing type 2 diabetes.
Leading an active lifestyle is key to preventing type 2 diabetes. Regular exercise can have a significant impact on your overall health and well-being. Engaging in physical activity not only helps with weight management but also improves insulin sensitivity, lowers blood sugar levels, reduces the risk of heart disease, and enhances cardiovascular health. In this section, we will explore the benefits of regular physical activity and provide practical tips to help you incorporate exercise into your daily routine to prevent type 2 diabetes.
Regular physical activity offers numerous benefits when it comes to preventing type 2 diabetes. Here are some key advantages of incorporating exercise into your routine:
Incorporating regular physical activity into your daily routine can significantly contribute to preventing type 2 diabetes and promoting overall health and well-being. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have existing health conditions or concerns.
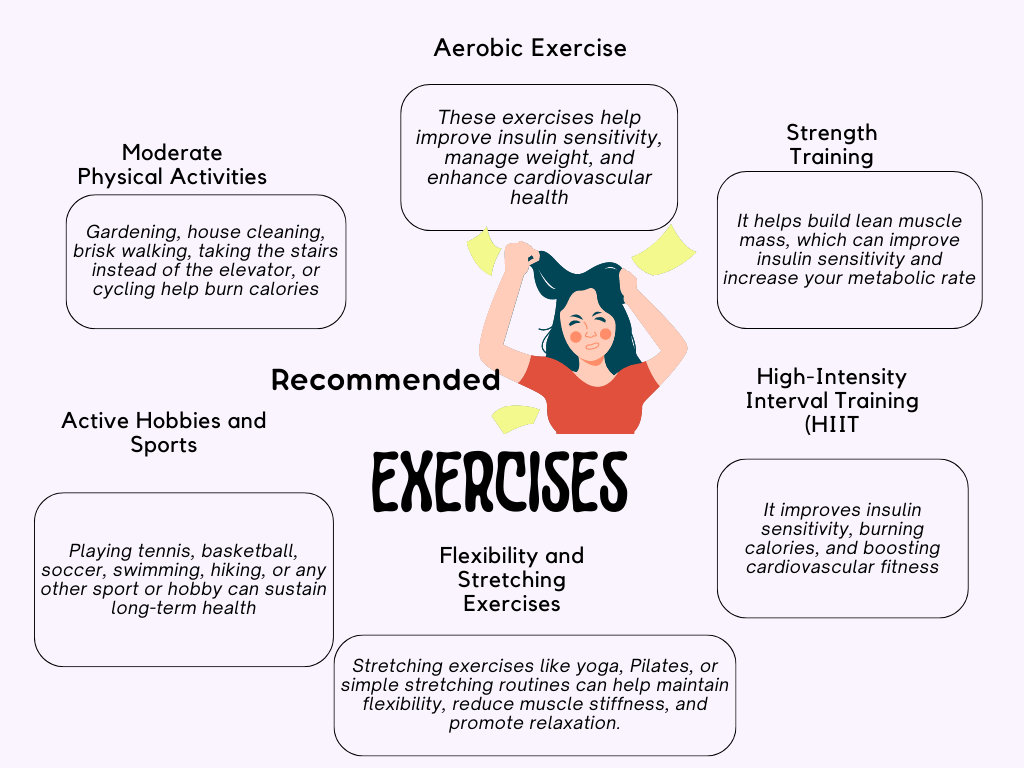
When it comes to preventing type 2 diabetes, a combination of aerobic exercise and strength training is recommended. Here are some types and durations of exercise that can help in diabetes prevention:
It’s important to start gradually and gradually increase the duration and intensity of your exercise routine. Listen to your body and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have underlying health conditions.
It’s also worth noting that consistency is key. Aim to make physical activity a regular part of your daily routine. If you’re new to exercise, seek guidance from a certified fitness professional to ensure you’re performing exercises correctly and safely.
By incorporating a variety of exercises and meeting the recommended durations, you can optimize your diabetes prevention efforts and enjoy the overall health benefits that physical activity provides.
Incorporating physical activity into your daily routine is essential for diabetes prevention. Here are some practical tips to help you make exercise a regular part of your life:
The key is to find activities that you enjoy and that fit into your lifestyle. Listen to your body, start at a comfortable level, and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your activities. Be consistent, and don’t be too hard on yourself if you miss a day or two—just get back on track as soon as possible.
Staying motivated and overcoming barriers to exercise can be challenging, but with the right strategies, you can maintain your commitment to physical activity. Here are some tips to help you stay motivated and overcome common barriers:
By applying these strategies, you can stay motivated and overcome barriers to exercise. Remember that consistency, perseverance, and a positive mindset are key to maintaining an active and healthy lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy weight is an essential aspect of diabetes prevention. Excess weight, especially around the waistline, significantly increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Calculate your body mass index (BMI) to determine a healthy weight range. Sustainable weight loss strategies include a combination of healthy eating, regular physical activity, portion control, and behavior change. Focus on making long-term lifestyle changes rather than relying on fad diets or quick fixes.
Focusing on weight management and adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Remember to consult with healthcare professionals or specialists for personalized guidance and recommendations based on your specific needs and circumstances.
The link between obesity and type 2 diabetes is well-established and significant. Obesity is recognized as one of the most significant risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes. When a person carries excess body weight, especially in the abdominal area, it can lead to hormonal imbalances, inflammation, and metabolic dysfunction, all of which contribute to insulin resistance.
Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. As a result, the pancreas produces more insulin to compensate for the resistance. Over time, the pancreas may become overworked and unable to produce enough insulin to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range. This leads to the development of type 2 diabetes.
It’s important to note that obesity does not guarantee the development of type 2 diabetes, and not all individuals with type 2 diabetes are obese. However, the risk of developing type 2 diabetes significantly increases with higher body mass index (BMI) and increased waist circumference.
Fortunately, weight loss and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% of total body weight can have a significant impact on improving insulin sensitivity and reducing the risk of diabetes. Combined with lifestyle modifications such as a healthy diet and regular physical activity, weight management is a crucial component of preventing and managing type 2 diabetes.
Calculating and determining a healthy weight can be done using various methods, but one commonly used indicator is the body mass index (BMI). The BMI is a numerical value derived from an individual’s height and weight and provides an estimate of body fatness. While it doesn’t directly measure body fat percentage, it is often used as a screening tool to assess weight status and potential health risks associated with weight.
To calculate your BMI, you can use the following formula:
BMI = weight (in kilograms) / (height (in meters) * height (in meters))
Alternatively, you can use online BMI calculators or consult with healthcare professionals who can assist you in determining your BMI.
Once you have your BMI value, it falls into one of the following categories:
Underweight: BMI below 18.5
Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9
Obesity: BMI of 30 or higher
While BMI is a useful initial assessment tool, it has limitations. It doesn’t take into account factors such as muscle mass, body composition, or distribution of fat. For individuals with higher muscle mass, such as athletes, BMI may not accurately reflect their level of body fat.
In addition to BMI, other factors to consider when determining a healthy weight include body composition, waist circumference, and individual health status. Body composition analysis, which measures the percentage of body fat, can provide a more accurate assessment of overall health and body fat distribution.
It’s important to note that a healthy weight is not solely determined by numbers on a scale. Optimal weight should be individualized based on factors such as body composition, overall health, genetics, and personal goals.
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight involves a combination of lifestyle changes, behavior modifications, and sustainable habits. Here are some effective strategies for weight loss and weight management:
Remember, weight loss is a journey that requires patience, persistence, and a long-term commitment to a healthy lifestyle. It’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians who can provide personalized guidance and support based on your individual needs and health conditions.
Behavior change and sustainable habits play a critical role in long-term weight control. While short-term diets or quick fixes may yield temporary results, lasting weight management requires a shift in behaviors and the adoption of sustainable habits. Here’s why behavior change is essential:
To promote behavior change and sustainable habits:
Remember, sustainable weight control is a lifelong commitment to healthy behaviors and self-care. It’s essential to be patient, forgiving of yourself, and willing to adapt as you navigate the ups and downs of behavior change.
Stress and lack of quality sleep have been associated with an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The body’s response to stress can lead to hormonal imbalances, elevated blood sugar levels, and insulin resistance. Additionally, inadequate sleep can disrupt the body’s regulation of appetite, leading to increased cravings for unhealthy foods and weight gain. Therefore, managing stress levels and establishing healthy sleep patterns are crucial for preventing type 2 diabetes. By incorporating stress management techniques and adopting good sleep hygiene practices, you can significantly reduce your risk.
1.Stress Management Techniques:
2.Healthy Sleep Habits:
By incorporating stress management techniques and prioritizing healthy sleep habits, you can improve your overall well-being, lower stress levels, regulate blood sugar levels, and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. It’s important to remember that managing stress and establishing good sleep patterns are ongoing practices that require consistency and commitment. By making them a priority in your daily life, you can greatly enhance your health and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Stress and sleep play interconnected roles in influencing diabetes risk. Chronic stress triggers the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol, which can lead to elevated blood sugar levels and insulin resistance over time. Prolonged exposure to stress can disrupt the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Additionally, insufficient or poor-quality sleep can impair the body’s insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Lack of sleep also affects appetite regulation, contributing to increased cravings for unhealthy foods and weight gain, both of which are risk factors for diabetes. Therefore, managing stress levels and prioritizing healthy sleep habits are crucial components of preventing type 2 diabetes, as they help maintain hormonal balance, regulate blood sugar, and support overall well-being.
There are various techniques for managing stress and improving emotional well-being, all of which can play a significant role in preventing type 2 diabetes. Here are some effective strategies:
Managing stress is an ongoing practice that requires patience and commitment. Implementing these techniques into your daily life can help reduce stress levels, improve emotional well-being, and significantly contribute to preventing type 2 diabetes.
Quality sleep is essential for overall health and plays a vital role in preventing type 2 diabetes. Here’s why quality sleep matters and some tips for establishing healthy sleep habits:
To establish healthy sleep habits, consider the following tips:
Prioritizing quality sleep and adopting healthy sleep habits, you can improve your overall well-being, support diabetes prevention efforts, and enhance your overall health. Remember, consistency is key, so aim to make these habits a regular part of your lifestyle.
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption not only harm your overall health but also increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake are essential steps towards prevention. Smoking damages blood vessels and affects insulin sensitivity, making it harder to control blood sugar levels. Reduce alcohol consumption to moderate levels, as excessive intake can lead to weight gain, liver damage, and disrupted blood sugar regulation.
1.Smoking and Type 2 Diabetes:
2.Alcohol Consumption and Type 2 Diabetes:
Taking steps to quit smoking and moderate alcohol intake can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and improve overall health. Here are some strategies:
1.Quit Smoking:
2.Moderate Alcohol Intake
By quitting smoking and moderating alcohol consumption, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and improve your overall health. Making these positive lifestyle changes supports your preventive efforts and contributes to a healthier future.
Smoking has a profound impact on diabetes risk, significantly increasing the chances of developing type 2 diabetes. The harmful chemicals present in tobacco smoke can disrupt the body’s insulin sensitivity and impair glucose regulation, leading to insulin resistance. Smoking is associated with higher levels of fasting blood sugar and an increased risk of developing diabetes even in individuals who are not overweight.
Moreover, smoking exacerbates the complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular diseases and kidney damage. The detrimental effects of smoking on the cardiovascular system further heighten the risk of developing diabetes by promoting inflammation and oxidative stress in the body. Quitting smoking is crucial for reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes and its associated complications, as it allows the body to regain insulin sensitivity and improve overall health.
The relationship between alcohol consumption and diabetes is complex. While moderate alcohol consumption may have some potential benefits, excessive or heavy drinking can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Alcohol can disrupt glucose regulation, leading to unstable blood sugar levels and insulin resistance. It can also contribute to weight gain, a significant risk factor for diabetes.
Moreover, excessive alcohol intake can damage the liver, impairing its ability to regulate blood sugar effectively. It is important to consume alcohol in moderation and be mindful of portion sizes to minimize the risk of diabetes. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals regarding alcohol consumption is advised.
Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol intake are crucial steps in promoting overall health and reducing the risk of developing diabetes. Here are some effective strategies for successfully making these lifestyle changes:
1.Quitting Smoking
2.Reducing Alcohol Intake
Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol intake are ongoing processes that require determination and perseverance. Celebrate small victories along the way and focus on the positive changes you are making for your health.
Regular health screenings and check-ups are crucial in detecting potential signs of diabetes and managing risk factors effectively. These screenings and check-ups play a vital role in identifying early warning signs, assessing overall health, and implementing preventive measures. During routine check-ups, healthcare professionals can conduct tests to measure blood sugar levels, assess body mass index (BMI), and evaluate other risk factors such as blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
By detecting any abnormalities or early signs of diabetes, individuals can take immediate action to prevent or manage the condition effectively. Regular check-ups also provide an opportunity for healthcare professionals to provide guidance on lifestyle modifications, offer personalized advice, and monitor progress in diabetes prevention efforts. By prioritizing regular health screenings and check-ups, individuals can take proactive steps to safeguard their health and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Regular medical check-ups and screenings play a crucial role in maintaining optimal health and preventing potential health issues, including diabetes. These routine appointments provide an opportunity for healthcare professionals to assess an individual’s overall well-being, identify risk factors, and detect early signs of diseases. Regular check-ups allow for the monitoring of key health indicators such as blood sugar levels, blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and body mass index (BMI).
By detecting any abnormalities or warning signs, healthcare professionals can intervene early, provide appropriate guidance, and implement preventive measures to manage or reduce the risk of developing diabetes. Furthermore, regular check-ups offer a platform for individuals to discuss their concerns, receive personalized advice, and gain a better understanding of their health status. By prioritizing regular medical check-ups and screenings, individuals can take a proactive approach towards maintaining their health, detecting potential health issues, and making informed decisions to prevent or manage diabetes effectively.
Several tests and examinations are commonly conducted to assess and monitor diabetes-related factors in individuals. These tests aid in diagnosing diabetes, evaluating its management, and assessing the risk of complications. Some common diabetes-related tests and examinations include:
These tests and examinations, along with regular medical check-ups, are important for individuals with diabetes to monitor their health status, evaluate treatment effectiveness, and identify any potential complications. It is recommended to discuss with healthcare professionals to determine the frequency and timing of these tests based on individual circumstances and medical history.
The frequency and timing of health screenings for diabetes prevention may vary based on individual risk factors, age, and overall health status. However, some general guidelines can help individuals stay on track with their preventive healthcare.
It is generally recommended to have regular check-ups with healthcare professionals at least once a year. During these annual visits, various diabetes-related screenings and tests can be conducted, including fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) test, lipid profile, and blood pressure measurement.
Additionally, individuals should consider more frequent screenings if they have specific risk factors such as a family history of diabetes, obesity, or a sedentary lifestyle. Regular eye examinations, foot examinations, and kidney function tests are also important components of diabetes prevention and should be incorporated into the screening schedule.
Ultimately, it is essential for individuals to consult with their healthcare professionals to determine the appropriate frequency and timing of health screenings based on their unique circumstances and healthcare needs.
Adopting healthy habits for diabetes prevention is a lifelong commitment. It requires consistent effort, dedication, and the ability to sustain lifestyle changes over the long term. Maintaining motivation is crucial in staying on track and making positive choices every day.
One effective way to stay motivated is by setting realistic and achievable goals. Breaking down larger goals into smaller, manageable steps can provide a sense of accomplishment and keep motivation levels high. It’s also important to celebrate progress and acknowledge the positive changes that have been made along the way. Surrounding oneself with a supportive network of family, friends, or a diabetes support group can provide encouragement, accountability, and a sense of community.
Additionally, finding enjoyment in physical activities and healthy eating can make it easier to maintain these habits. Incorporating variety and trying new things can help prevent monotony and keep motivation levels high.
Lastly, focusing on the long-term benefits of diabetes prevention, such as improved overall health and a reduced risk of complications, can serve as a powerful motivator. By staying committed, seeking support, and finding joy in healthy choices, individuals can make sustainable lifestyle changes that contribute to their long-term success in preventing type 2 diabetes.
Setting realistic goals and tracking progress are essential components of maintaining motivation and making sustainable lifestyle changes for diabetes prevention. When setting goals, it is important to make them specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Breaking down larger goals into smaller, actionable steps helps maintain focus and provides a sense of accomplishment along the way. Regularly tracking progress allows individuals to see their efforts paying off and provides motivation to continue. This can be done through various methods, such as keeping a food and activity diary, using smartphone apps, or utilizing fitness trackers.
Celebrating milestones and acknowledging achievements, no matter how small, further boosts motivation and reinforces positive behaviors. By setting realistic goals and regularly monitoring progress, individuals can stay motivated, stay on track with their diabetes prevention efforts, and make long-lasting lifestyle changes.
Staying motivated and overcoming setbacks is crucial when striving for long-term success in diabetes prevention. One effective strategy is to find intrinsic sources of motivation, such as focusing on the personal benefits of a healthy lifestyle, improved well-being, and increased energy levels. It can also help to remind oneself of the negative consequences of not taking preventive measures.
Additionally, finding external sources of motivation, such as joining a support group or enlisting the support of friends and family, can provide encouragement and accountability. When facing setbacks, it is important to view them as learning opportunities rather than failures. Reflecting on the challenges, identifying the underlying reasons for the setback, and adjusting the approach accordingly can help individuals regain momentum. It’s also helpful to set realistic expectations and be kind to oneself throughout the process.
Practicing self-compassion and focusing on progress rather than perfection can help maintain motivation during challenging times. Ultimately, staying motivated requires a mindset of resilience, perseverance, and the belief that each day is an opportunity to make positive choices and work towards diabetes prevention.
Building a support system and seeking professional guidance are important strategies in diabetes prevention. Surrounding oneself with a supportive network of family, friends, or a diabetes support group can provide encouragement, understanding, and motivation. Sharing experiences, challenges, and successes with others who are also on a similar journey can create a sense of community and foster a positive environment for making sustainable lifestyle changes.
Additionally, seeking professional guidance from healthcare professionals, such as doctors, dietitians, or diabetes educators, can provide valuable expertise and personalized advice. These professionals can offer guidance on nutrition, exercise, weight management, and stress management techniques specific to diabetes prevention.
They can also help monitor progress, provide accountability, and make necessary adjustments to the prevention plan. By building a support system and seeking professional guidance, individuals can feel supported, empowered, and equipped with the knowledge and tools to make informed decisions and successfully prevent type 2 diabetes.
In this comprehensive guide, we have explored the key lifestyle changes and habits that play a vital role in preventing type 2 diabetes. We began by understanding the nature of type 2 diabetes and its risk factors, emphasizing the importance of early prevention. We then delved into the significance of healthy eating, highlighting the role of a balanced diet, the impact of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, and providing recommendations for foods to include and avoid. We discussed practical tips for meal planning and portion control to maintain a healthy eating routine.
Additionally, we emphasized the importance of regular physical activity and exercise, highlighting their benefits, recommended types and durations, and strategies for incorporating them into daily life. We addressed the role of weight management in diabetes risk reduction and provided effective strategies for weight loss and long-term weight control.
Furthermore, we emphasized the connection between stress, sleep, and diabetes risk, providing techniques for managing stress, establishing healthy sleep habits, and promoting emotional well-being. We explored the impact of smoking and alcohol consumption on diabetes risk and offered strategies for quitting smoking and reducing alcohol intake. Lastly, we discussed the importance of regular health screenings, tracking progress, building a support system, and seeking professional guidance for diabetes prevention.
It is crucial to recognize that preventing type 2 diabetes requires a commitment to making positive lifestyle changes and adopting sustainable habits. By implementing these lifestyle changes and habits, you can take control of your health and significantly reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Remember, small steps and consistent efforts can lead to significant long-term benefits. Take action today and prioritize your health and well-being. Your future self will thank you.
Closing sentence: “By implementing these lifestyle changes and habits, you can take control of your health and significantly reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.”
If you’ve ever tried to lose weight but felt sabotaged by cravings, stress, or poor sleep, you’re not alone. Hormonal weight gain – especially belly
Welcome to our WealthGenix review! If you’re looking to boost your mental clarity, energy, and overall well-being, you might be curious about WealthGenix. With a